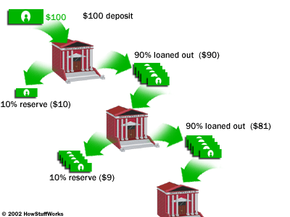
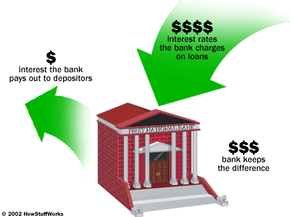
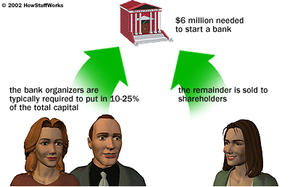
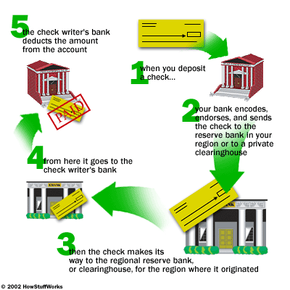
There are still some details that have to be determined before you can submit your charter application. For instance, what are you going to call your bank? You have to come up a with a name that is different enough from other bank names to avoid confusion. You also need to think about whether you want the word "bank" in the name, and whether you want the geographic region in the name. Regardless of the name you choose, you have to verify that the name is not being used by any other corporations -- which leads us to the fact that you have to become incorporated.
Before you actually file your application, it is recommended that you set up a pre-filing meeting with the state's department of finance and banking. This will help make sure that you have all of the information you need to file. Usually, the biggest delays come from incomplete background and/or financial information.
Once you have all of the details ironed out, you fill out the charter application and submit it (along with a lot of other information) to the state's board of finance and banking -- or, if you're applying for a federal charter, you'll send it to the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency. Here is the list of items you have to include in Florida:
- The names and addresses of all of the organizers and the holding company (if there is one)
- The names of the proposed directors, the CEO, the senior loan officer and the cashier
- The name and address of the bank
- The number of shares, par value, and share prices for each share that will be sold
- The total amount of common stock, as well as surplus and reserves for operating expenses
- The number of shares of bank stock that each organizer plans to purchase
- Where the money for purchasing those shares is coming from
- Names and addresses of proposed investors who will own more than 10 percent of the bank's total stock
- A completed charter application (form DBF-C-10 in Florida) for each organizer, proposed director and principal stockholder, CEO, senior loan officer, cashier, and all other executive officers
- Pro forma financial statements
- An addendum to those financial statements that explains assumptions and strategies to achieve the projected market share for each type of product or service
- Assumptions used to calculate earnings
- Everyone involved in the purchase or lease of the proposed bank building
- Any business or personal affiliations between the bank property seller or lessor and any of the organizers, other bank officers, and shareholders who will own 10 percent or more of the bank stock
- Copies of location feasibility studies and local zoning laws
- Copies of results of any environmental tests conducted at the bank's location
- Projected organization costs (this includes filing and regulatory fees, professional and consulting fees, payroll and payroll taxes, rent, capital-raising costs, printing, postage, telephone and office supplies)
- Proposed salaries and benefits for bank officers
- Copies of any employment contracts that may be given to officers
- Copies of proposed bank policies
- And finally, your detailed business plan!
As you can see, there is a lot of information that has to be gathered and submitted with your charter application. Leaving out any of this information, or having some of it incomplete, will slow down the review process considerably. There will also be a filing fee, which in Florida is $15,000. Most other states require a similar amount.
If your application is deemed complete, then a decision will be given within 180 days. If your charter is granted, you will usually have up to one year to open your bank. In all states, you are required to apply for deposit insurance with the FDIC before you can accept deposits from the public.